springboot启动流程
大致流程图
springboot的入口程序
@SpringBootApplication
public class SampleWebServicesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SampleWebServicesApplication.class, args);
}
}
run静态方法会先创建一个spring应用对象.再执行具体的应用对象的run方法.
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
创建springboot应用对象
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 1. 资源初始化资源加载器,默认为null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 2. 初始化主要加载资源类集合并去重
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 3. 推断当前 WEB 应用类型,一共有三种:NONE,SERVLET,REACTIVE
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 4. 初始化 引导注册表初始化后增强器
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories();
// 5. 设置应用初始化器, 从MATE-INF/spring.factories中读取ApplicationContextInitializer类的实例名称集合并去重.(七个)
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 6. 设置监听器, 从MATE-INF/spring.factories中读取ApplicationListener类的实例名称集合并去重.(十一个)
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 7. 推断主入口应用类,通过当前调用栈,获取Main方法所在类,并赋值给mainApplicationClass
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
3. 判断web应用类型
通过判断是否存在特定类来标识程序类型.
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
// 存在响应式调度器对象,且不存在服务调度程序对象与程序容器类. 则是响应式程序.
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
// 如果不存在servlet程序对象或者web服务容器对象. 则是啥也不是.
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
// 否则为web程序.
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
4. 初始化 应道注册表初始化后增强器
用于提前创意一些初始化时用到的必要参数与对象.比如springcloud会在bootstrap.yml中定义配置中心地址,来远程获取并加载后续初始化用到的参数.
private List<BootstrapRegistryInitializer> getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories() {
ArrayList<BootstrapRegistryInitializer> initializers = new ArrayList<>();
// 是否存在bootstrapper类型的class类,若存在则实例化后,生成初始化器,并加入列表.
getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class).stream()
.map((bootstrapper) -> ((BootstrapRegistryInitializer) bootstrapper::initialize))
.forEach(initializers::add);
// 是否存在bootstrap的注册初始化器的class类.若存在则创建对象并加入列表.
initializers.addAll(getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
return initializers;
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 通过calss类型来去重获取具体实现类名称,通过扫描所有jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories文件.
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 实例化实现类.
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// 将实现类对象排序.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
/**
* 接收calss名称列表.类加载器找寻指定类,并通过反射来实例化对象输出.
*/
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
// 通过class类名来获取class对象.
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
// 获取calss对象中的构造器.
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
// 实例化对象,通过构造函数与指定参数.
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
// 返回实例化对象列表.
return instances;
}
5. 设置应用初始化器
通过反射将各个包中的ApplicationContextInitializer类找出并初始化后添加进集合.
一般是七个加载器:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer
创建一个SpringBoot和ConfigurationClassPostProcessor共用的CachingMetadataReaderFactory对象。
实现类为:ConcurrentReferenceCachingMetadataReaderFactory
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer
委派处理ApplicationContext初始化器.
其需要委派处理的初始化器来自Spring环境中的context.initializer.classes属性,该属性可以使用逗号分隔多个初始化器。
- org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer
为ApplicationContext设置id。
根据以下的配置顺序来设置,spring.application.name、vcap.application.name、spring.config.name,如果环境配置中都没有这些配置,则默认使用“application”来表示,另外还会将profiles也加入到id中去。
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
将ConditionEvaluationReport写入日志。
- org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer
对于一般配置错误在日志中作出警告
- org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
为RSocketServer服务器实际监听的端口设置环境属性。
- org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
其主要作用是在环境Environment中添加一个属性源,将应用的本地端口号添加进去.
6. 设置监听器
通过反射将各个包中的ApplicationListener类找出并初始化后添加进集合.
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor
CloudFoundryVcap环境变量的后置处理器.
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener
配置文件解析的监听器.
- org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener
Ansi输出应用监听器. 应用环境准备就绪事件时,对Ansi输出的相关状态进行设置.
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener
初始化sb的logging级别,根据环境变量初始化系统,确定最终的logging等级,注册shutdown的钩子方法。
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
后台初始化ConversionServiceInitializer、ValidationInitializer、MessageConverterInitializer、JacksonInitializer、CharsetInitializer组件
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener
通过环境中的配置的context.listener.classes,去搜集相应的监听器。如果收集到,就会创建一个简单事件广播器实例,放到类属性上,同时,还会把收集到的监听器,绑定到该广播器上。
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener
文件编码应用监听器。该监听器实质作用是在收到应用环境准备就绪事件时,对配置中关于文件编码的配置作一个校验,判断配置中的文件编码是否和JVM系统的file.encoding一致。无配置或JVM系统的file.encoding无效的情况下,都不会报异常,但是,当JVM中的file.encoding有效,且在配置中包含了spring.mandatory-file-encoding,而二者又不一致时报IllegalStateException异常。
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
7. 寻找程序主方法
通过异常栈,遍历栈,寻找出main的class类并返回.
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
// 获取run方法执行的堆栈信息
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
// 遍历堆栈信息
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
// 寻找方法名称为main的所在类.
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
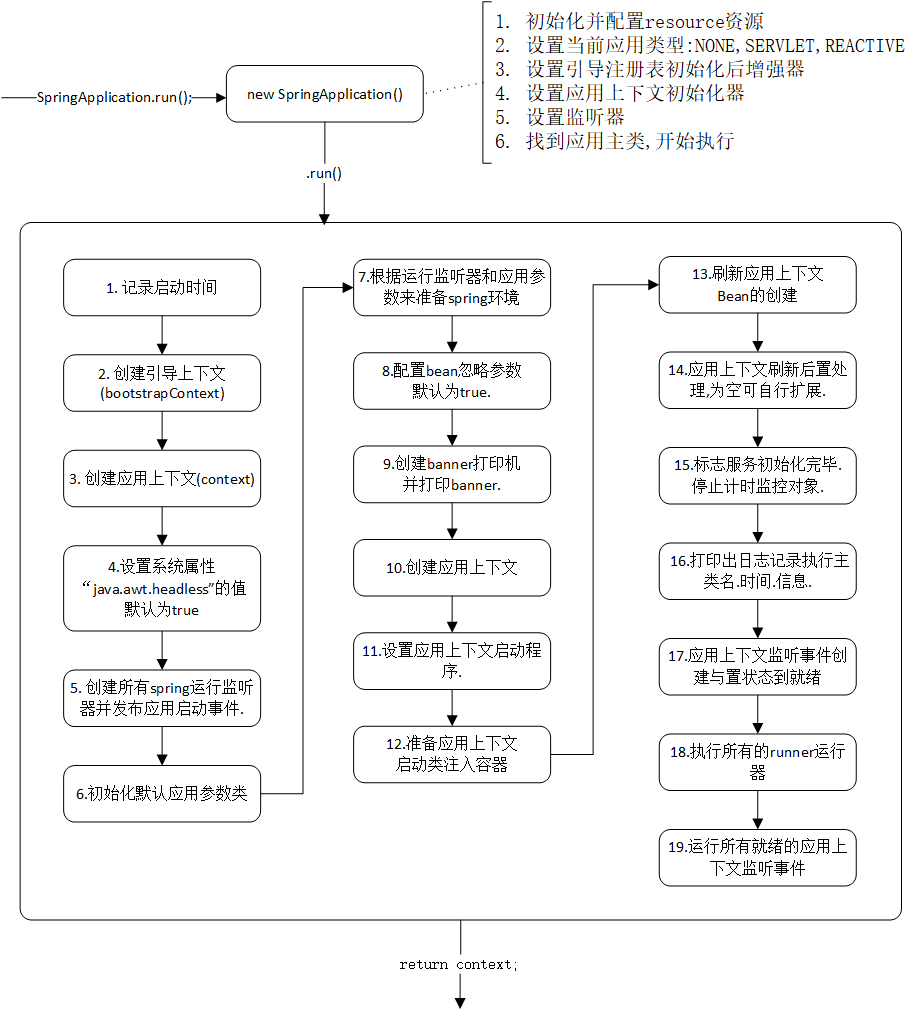
执行应用对象的run方法.
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 1.记录启动时的时间.
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 2.创建引导上下文
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
// 3.初始化应用上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 4.设置系统属性“java.awt.headless”的值,默认为true,
// 用于运行headless服务器,进行简单的图像处理,多用于在缺少显示屏、键盘或者鼠标时的系统配置,很多监控工具如jconsole 需要将该值设置为true
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 5.创建所有spring运行监听器并发布应用启动事件.
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
// 6.初始化默认应用参数类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 7.根据运行监听器和应用参数来准备spring环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
// 8.配置bean忽略参数,默认为true.
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 9.创建banner打印机,并打印banner.
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 10.创建应用上下文.
context = createApplicationContext();
// 11.设置应用上下文启动程序.
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 12.准备应用上下文. 关键步骤:将启动类注入容器,为后续启动话提供基础.
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 13.刷新应用上下文
refreshContext(context);
// 14.应用上下文刷新后置处理,为空可自行扩展.
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 15.标志服务初始化完毕.停止计时监控对象.
stopWatch.stop();
// 16.记录启动信息状态为true时,打印出日志记录执行主类名.时间.信息.
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 17.应用上下文监听事件创建与置状态到就绪.
listeners.started(context);
// 18.执行所有的runner运行器.
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 19.运行所有就绪的应用上下文监听事件
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 20.返回上下文.
return context;
}
2.创建引导上下文
Spring Boot 启动开始阶段,需要初始化一些东西,这个时候并不会直接创建ApplicationContext,而是先创建BootstrapContext,在ApplicationContext完全创建好之前负责启动和准备环境(Environment)的一些操作。
其本身是一个简单的ioc容器,提供了bean注册与获取的方法, 作用是在启动阶段,创建一个引导性质的容器,先去负责一些初始化操作。
private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {
// 创建DefaultBootstrapContext 对象
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();
// 循环调用BootstrapRegistryInitializer对象的初始化方法
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.initialize(bootstrapContext));
return bootstrapContext;
}
DefaultBootstrapContext
类图如下显示,DefaultBootstrapContext实现了BootstrapRegistry和BootstrapContext接口.
BootstrapRegistry 就提供了在启动开始阶段,ApplicationContext完全创建好之前,负责Bean 实例注册的功能。
BootstrapContext 是提供bean对象的获取接口,通过反射的形式.

5.创建所有spring运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String...)
// 创建所有spring运行监听器具体实例
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 执行监听并发布应用启动事件.
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
/**
* org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication实现方法
*/
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
// 创建一个数组,存放SpringApplication.class、String[].class
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
// 通过SPI机制,从spring.factories 中获取SpringApplicationRunListener实例,并保存在SpringApplicationRunListeners对象中.
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args),
this.applicationStartup);
}
/**
* org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners类
*/
SpringApplicationRunListeners(Log log, Collection<? extends SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners,
ApplicationStartup applicationStartup) {
this.log = log;
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
this.applicationStartup = applicationStartup;
}
/**
* 开启监听器.声明listenerAction函数与stepAction函数
*/
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class<?> mainApplicationClass) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),
(step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
});
}
// doWithListeners
/**
* 遍历在创建appicationContext时,通过spi机制获取到的监听器对象.
*/
private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction,
Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {
StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);
this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);
if (stepAction != null) {
stepAction.accept(step);
}
step.end();
}
7~9. 根据运行监听器和应用参数来准备spring环境
// 6.初始化默认应用参数类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 7.根据运行监听器和应用参数来准备spring环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
// 8.配置bean忽略参数,默认为true.
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 9.创建banner打印机,并打印banner.
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
初始化参数
创建参数获取接口对象.
// org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments
public interface ApplicationArguments {
// 返回传递给应用程序的原始未处理参数
String[] getSourceArgs();
// 返回所有选项参数的名称
Set<String> getOptionNames();
// 返回从参数解析的选项参数集是否包含具有给定名称的选项
boolean containsOption(String name);
// 返回与具有给定名称的参数选项关联的值的集合
List<String> getOptionValues(String name);
// 返回已解析的非选项参数的集合
List<String> getNonOptionArgs();
}
spring环境接口对象
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
// 设置当前激活的配置文件
void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles);
// 增加profile
void addActiveProfile(String profile);
// 设置默认的profile
void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles);
// 获取PropertySource键值组合的集合
MutablePropertySources getPropertySources();
// 获取系统属性
Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties();
// 获取系统环境变量
Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment();
// 合并其他 ConfigurableEnvironment
void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent);
}
创建环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 1.创建环境,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 2.配置环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 3.连接
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 4.调用监听器
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
// 5.将 defaultProperties 移到最后位置
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
// 6. 绑定信息
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 没有设置 isCustomEnvironment 属性,
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
// 环境转换
environment = convertEnvironment(environment);
}
// 重新连接
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
创建环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() { // 如果环境已经初始化,则直接返回 if (this.environment != null) { return this.environment; } // 判断环境的类型,更具不同的类型返回不同的实例对象. switch (this.webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: return new ApplicationServletEnvironment(); case REACTIVE: return new ApplicationReactiveWebEnvironment(); default: return new ApplicationEnvironment(); } }配置环境
对属性、Profile 进行配置
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) { // 设置转换服务 if (this.addConversionService) { environment.setConversionService(new ApplicationConversionService()); } // 配置属性 configurePropertySources(environment, args); // 配置profile configureProfiles(environment, args); } // 配置属性 protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) { // 获取所有的属性源 MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultProperties)) { DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.addOrMerge(this.defaultProperties, sources); } // 是否添加启动命令参数,默认True if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) { String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME; if (sources.contains(name)) { PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name); CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name); composite.addPropertySource( new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args)); composite.addPropertySource(source); sources.replace(name, composite); } else { sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args)); } } } // configureProfiles则是一个空的方法,没有实现,所以配置环境这一步主要也是获取其他方面的属性。 protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) { }连接
将环境中的
PropertySources封装到一个名称为configurationProperties的PropertySource中.public static void attach(Environment environment) { Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment); // 获取环境中的 PropertySources MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment).getPropertySources(); // 判断 是否有configurationProperties,之前加载的四个是没有这个名字的所以为NULL PropertySource<?> attached = getAttached(sources); if (attached == null || !isUsingSources(attached, sources)) { // 创建一个configurationProperties。 attached = new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources)); } sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); // 将configurationProperties 设置到第一位置 sources.addFirst(attached); }调用监听器
// 调用监听器 // [org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener@434a63ab] listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment); // org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { // 创建指定事件给监听器执行. this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent( new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args, environment)); } // org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster @Override public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event)); Executor executor = getTaskExecutor(); // 支持事件的监听器,执行事件. for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) { if (executor != null) { executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event)); } else { invokeListener(listener, event); } } }该阶段对应的事件类型为
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent,支持该事件的监听器有六种:
- org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
- org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener
主要处理逻辑在EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener中
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) { // 获取当前环境和SpringApplication ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment(); SpringApplication application = event.getSpringApplication(); // SPI 获取环境后置处理器,并调用处理 for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : getEnvironmentPostProcessors(application.getResourceLoader(), event.getBootstrapContext())) { postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(environment, application); } } List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> getEnvironmentPostProcessors(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) { ClassLoader classLoader = (resourceLoader != null) ? resourceLoader.getClassLoader() : null; EnvironmentPostProcessorsFactory postProcessorsFactory = this.postProcessorsFactory.apply(classLoader); return postProcessorsFactory.getEnvironmentPostProcessors(this.deferredLogs, bootstrapContext); }环境后置处理器:
org.springframework.boot.env.RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
添加
RandomValuePropertySource属性源,可以通过environment.getProperty("random.*")返回各种随机值。org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
将之前加载的系统属性对象
SystemEnvironmentPropertySource替换为一个新的对象OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySourceorg.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
解析
spring.application.json或SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON配置的 json 字符串。org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor
配置
Cloud Foundry开源PaaS云平台相关属性源。org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor
启用 Reactor 调试代理(如果可用)。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationPropertiesEnvironmentPostProcessor
将
META-INF/spring.integration.properties中的属性映射为属性源。org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor
将
application.yml文件中的属性加载到环境中的
其中最重要的就是
ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor,就是用它将application.yml文件中的属性加载到环境中的,加载完成后可以看到你在application.yml文件中配置的所有属性.将 defaultProperties 移到最后位置
// 5.将 defaultProperties 移到最后位置 DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment); // 查找配置文件源中的defaultProperties,删除它, // 如果没找到说明程序没有启用properties配置文件,则需要返回null,来避免下一步的添加默认Properties配置. public static void moveToEnd(MutablePropertySources propertySources) { PropertySource<?> propertySource = propertySources.remove(NAME); // 如果配置列表不为null,并在最后重新添加. if (propertySource != null) { propertySources.addLast(propertySource); } }绑定信息
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { try { Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(this)); } catch (Exception var3) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", var3); } }